parent
70bc2a1038
commit
e0ae5dd309
3 changed files with 212 additions and 1 deletions
@ -0,0 +1,181 @@ |
||||
--- |
||||
title: 'Data Science vs Machine Learning: How are they different?' |
||||
description: 'Excited about a career in data science or machine learning? Learn the differences, key skills, tools, and how to choose the role that aligns with your ambitions' |
||||
authorId: ekene |
||||
excludedBySlug: '/ai-data-scientist/vs-machine-learning' |
||||
seo: |
||||
title: 'Data Science vs Machine Learning: How are they different?' |
||||
description: 'Excited about a career in data science or machine learning? Learn the differences, key skills, tools, and how to choose the role that aligns with your ambitions.' |
||||
ogImageUrl: 'https://assets.roadmap.sh/guest/data-science-vs-machine-learning-gaa7s.jpg' |
||||
isNew: true |
||||
type: 'textual' |
||||
date: 2025-02-06 |
||||
sitemap: |
||||
priority: 0.7 |
||||
changefreq: 'weekly' |
||||
tags: |
||||
- 'guide' |
||||
- 'textual-guide' |
||||
- 'guide-sitemap' |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
If you're excited by the idea of extracting insights from data to guide decisions, a career in [data science](https://roadmap.sh/ai-data-scientist) might be for you. On the other hand, if you're drawn to creating the algorithms behind AI systems and building intelligent applications, machine learning could be your ideal path. |
||||
|
||||
Both fields are at the forefront of innovation, driving transformative technologies like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Gemini. These advancements, used across industries like healthcare, finance, and tech, owe their success to the growing collaboration between data science and machine learning. As AI becomes more accessible with tools from companies like OpenAI and AWS, the demand for experts in these fields is only increasing. |
||||
|
||||
So, how do you choose between these high-demand, rewarding careers? As an ML Engineer with experience on projects that span across data science and machine learning, I have gained a deep understanding of the overlaps and differences between these fields. In this guide, I will explain the responsibilities of each role, highlight their key differences, and outline the essential skills for success. By the end, you'll be better equipped to pick the path that matches your interests, strengths, and career goals. |
||||
|
||||
The table below summarizes the key differences between data science and machine learning you should consider to help you evaluate which one best fits your career goals: |
||||
|
||||
| **Aspect** | **Data science** | **Machine learning** | |
||||
| ------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
||||
| **Ideal for you** **i\*\***f\***\*…** | You enjoy exploring and analyzing data to extract insights and inform decisions. | You are passionate about creating algorithms and systems that learn and improve automatically. | |
||||
| **Educational background** | Strong foundation in statistics, data analysis, and visualization tools. | Strong foundation in mathematics, programming, and AI techniques. | |
||||
| **Career opportunities** | Data scientist, [Data Analyst](https://roadmap.sh/data-analyst), Business Intelligence Analyst. | Machine learning Engineer, AI Researcher, Deep Learning Specialist. | |
||||
| **Industries** | Healthcare, finance, marketing, e-commerce, and government sectors. | Technology, autonomous systems, robotics, fintech, and R&D labs. | |
||||
| **Skills you'll need** | Data cleaning, exploratory analysis, storytelling, and domain expertise. | Proficiency in machine learning libraries, algorithm design, and optimization. | |
||||
| **Growth potential** | Strong demand across industries as companies seek to become more data-driven. | High demand in tech-driven fields as AI adoption accelerates. | |
||||
| **Creativity vs. technical** | Balances creativity in visualizations with technical skills in data processing. | Heavily focused on technical and mathematical skills for problem-solving and predictive analytics. | |
||||
| **Long-term vision** | Perfect if you want to lead data-driven strategy or explore business analytics. | Ideal if you aim to innovate in AI, robotics, or advanced tech solutions. | |
||||
|
||||
Before looking at these features in detail, let's take a closer look at these two fields. |
||||
|
||||
## What is data science? |
||||
|
||||
Data science is a field that combines techniques from statistics, domain knowledge, computer science, and data analysis to gain insights from structured and unstructured data. As a data scientist, you'll use tools, machine learning models, and algorithms to understand data and drive decision-making. You'll use these insights to help businesses increase profits, create innovative products and services, improve systems, and solve problems across various industries. |
||||
|
||||
**Key Components of Data Science** |
||||
The key components of data science involve the following processes: |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
1. **Data collection**: The first step is to gather raw data from various sources such as APIs, sensors, databases, and web scraping. |
||||
2. **Data cleaning and preparation**: After collecting the raw data, it must be cleaned by removing inaccuracies, handling missing values, and formatting it for analysis. |
||||
3. **Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)**: Use statistical methods and visualization techniques to explore the data, identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, and gain a better understanding of the dataset. |
||||
4. **Data modeling and machine learning**: Apply machine learning algorithms to build models that can identify patterns, predict outcomes, and automate processes. |
||||
5. **Data visualization**: Use tools like charts, graphs, and dashboards to present insights and communicate findings clearly to stakeholders. |
||||
6. **Deployment and monitoring**: Implement data models in real-world applications and continuously monitor their performance to ensure they remain accurate and effective. |
||||
|
||||
### Essential Skills and Tools You Need for a Successful Data Science Career |
||||
|
||||
To build a successful career in data science, knowledge of a programming language like [Python](https://roadmap.sh/python) is essential. Beyond that, as a data scientist, you'll need to develop expertise in the following skills and tools: |
||||
|
||||
- **Programming languages**: You'll need proficiency in [SQL](https://roadmap.sh/sql), R, SAS, and others to collect, manipulate, and manage both structured and unstructured data. |
||||
- **Mathematics, statistics, and probability**: A strong grasp of these concepts will enable you to build accurate models and make data-driven decisions with confidence. |
||||
- **Data wrangling and visualization**: You'll be responsible for cleaning, transforming, and visualizing data using tools like Matplotlib, Seaborn, Power BI, and Tableau to present insights effectively. |
||||
- **Machine learning and predictive modeling**: Knowledge of machine learning algorithms and techniques for building models that can make predictions and automate decision-making processes. |
||||
- **Data analysis tools**: Familiarity with tools like Jupyter Notebooks, Pandas, NumPy, Apache Spark, and Scikit-learn will help you analyze and process data with ease. |
||||
- **Cloud platforms**: Experience with cloud platforms such as [AWS](https://roadmap.sh/aws), Azure, and Google Cloud will enable you to leverage cloud resources for scalable computing and efficient model deployment. |
||||
|
||||
## What is machine learning? |
||||
|
||||
Machine learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. Rather than manually coding rules for every scenario, machine learning models learn from available data to perform tasks such as fraud detection, recommendation systems, natural language processing, and image recognition. It can be broadly categorized into the following types: |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
- **Supervised learning**: In supervised learning, you train a model labeled data to predict outcomes and identify patterns. For example, you can use a dataset with details like location, square footage, and other factors to teach the model how to predict house prices. |
||||
- **Unsupervised learning**: In unsupervised learning, the model is trained on unlabeled data and discovers patterns or groupings on its own. For example, you can use it to segment customers based on their purchasing habits without specifying predefined categories. |
||||
- **Reinforcement learning**: In reinforcement learning, you train a model through a trial-and-error process to achieve the best outcomes. For instance, self-driving cars use reinforcement learning by continuously learning to recognize obstacles, road signs, and blockages through repeated experiences. |
||||
|
||||
### Key Components of Machine Learning |
||||
|
||||
The key components of machine learning involve the following processes: |
||||
|
||||
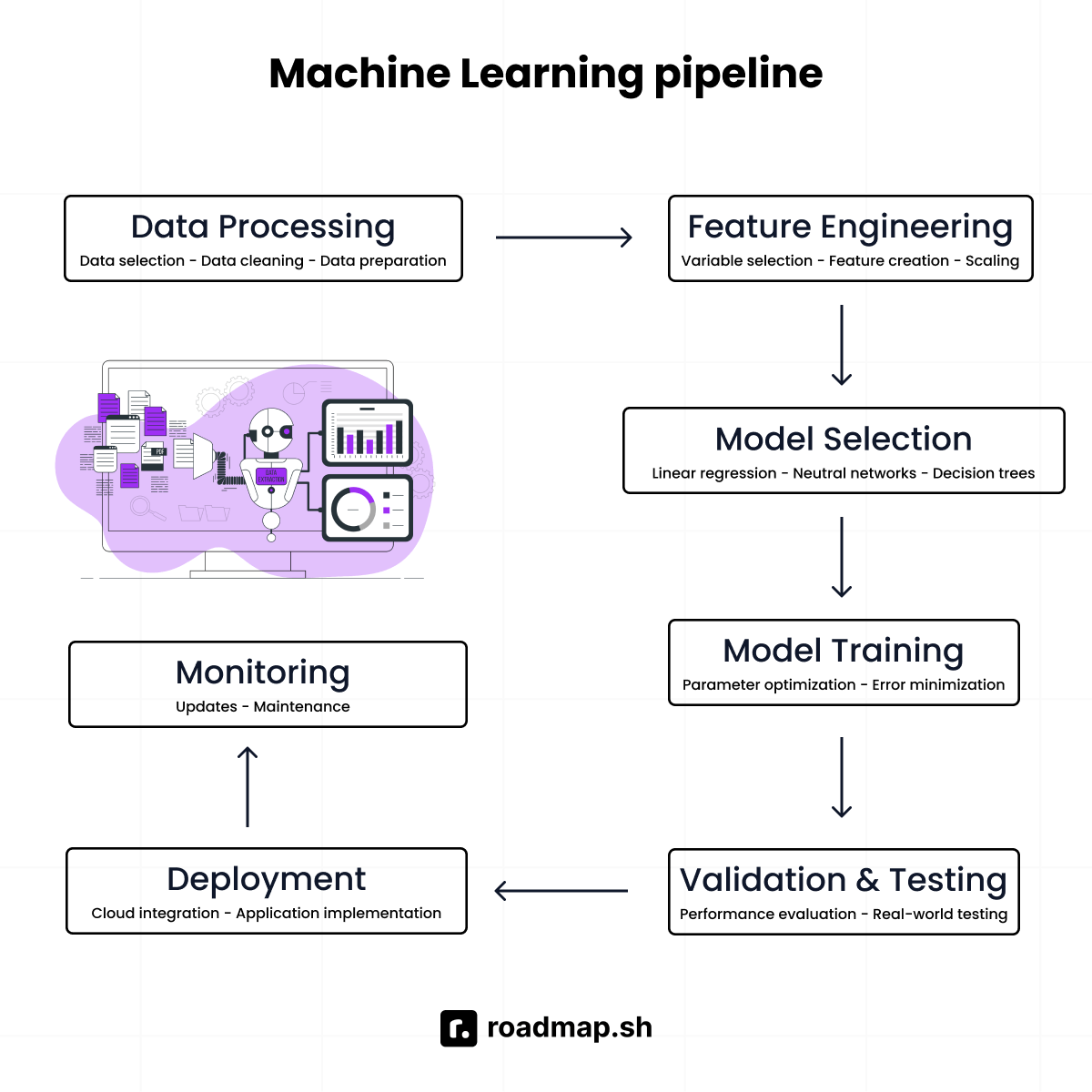 |
||||
|
||||
1. **Data processing**: The foundation of any machine learning system is data. For the model to work effectively, it requires selecting and preparing the right data for training. |
||||
2. **Feature engineering**: This step involves selecting the right variables (features) that the model can use to make accurate predictions. For example, a housing price prediction model would need features like the number of bedrooms, square footage, and location to make reliable predictions. |
||||
3. **Model selection**: Choosing the appropriate model for a specific task is crucial. For instance, a **Linear Regression** model is suitable for predicting continuous values, while **Neural Networks** are better suited for tasks like image recognition. |
||||
4. **Model training**: In this process, the selected model is fed with training data to help it learn patterns. The model's internal parameters are adjusted to minimize prediction errors. |
||||
5. **Validation and testing**: After training, the model's performance is evaluated using a separate validation dataset. A final test dataset is used to ensure the model performs well in real-world scenarios. |
||||
6. **Deployment**: Once the model is ready, it is integrated into real-world applications or deployed on cloud platforms to be accessed by third party users. |
||||
7. **Model monitoring and maintenance**: After deployment, the model must be regularly monitored and updated to maintain accuracy and adapt to changes over time. |
||||
|
||||
### Essential Skills and Tools You Need for a Successful Machine Learning Career |
||||
|
||||
To build a successful career in machine learning, you'll need to develop the following essential skills and become familiar with key tools: |
||||
|
||||
- **Strong understanding of mathematics and statistics**: You'll need a solid understanding of linear algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics to grasp how machine learning algorithms function. |
||||
- **Proficiency in programming languages**: Python and R are must-haves for implementing machine learning models and handling data efficiently. |
||||
- **Data handling and preprocessing skills**: You need a solid understanding of how to clean, preprocess, and transform raw data into a format suitable for training models. |
||||
- **Knowledge of machine learning algorithms**: Understanding algorithms like Linear Regression, Q-learning, and K-means and knowing when to apply them will help you tackle diverse challenges. |
||||
- **Model evaluation and tuning**: You need to master techniques to evaluate model performance (e.g., accuracy, precision, recall) and fine-tune hyperparameters to improve results. |
||||
- **Familiarity with libraries and frameworks**: Hands-on experience with Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras, and other popular libraries and frameworks will help you build and deploy machine learning models efficiently. |
||||
- **Cloud Platforms for Infrastructure**: Familiarity with cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure will let you manage the infrastructure needed for large-scale machine learning projects. |
||||
|
||||
While data science and machine learning share common skills, tools, and workflows, they differ significantly in their approaches, methodologies, and focus areas. The table below summarizes the key differences between machine learning and data science: |
||||
|
||||
| **Category** | **Data science** | **Machine learning** | |
||||
| ------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | |
||||
| **Mathematics and statistics** | Strong knowledge of statistics, probability, and linear algebra. | Deep understanding of calculus, linear algebra, and optimization techniques. | |
||||
| **Programming languages** | Python, R, and SQL for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and visualization. | Python, [C++](https://roadmap.sh/cpp), and [Java](https://roadmap.sh/java) for implementing machine learning algorithms. | |
||||
| **Data handling** | Data wrangling, data cleaning, and data visualization. | Data preprocessing, feature engineering, and handling large datasets. | |
||||
| **Machine learning basics** | Basic understanding of supervised, unsupervised learning, and regression. | Advanced knowledge of machine learning algorithms, including deep learning. | |
||||
| **Business acumen** | Ability to translate business problems into data solutions. | Focus on technical problem-solving without a primary business context. | |
||||
| **Tools and frameworks** | Tableau, Excel, Hadoop, Pandas, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn. | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn, Keras, and XGBoost. | |
||||
| **Data visualization** | Building dashboards, reports, and storytelling through data. | Creating visualizations primarily for model performance evaluation. | |
||||
| **Communication skills** | Strong emphasis on presenting insights to non-technical stakeholders. | Less focus on communication; more technical documentation. | |
||||
| **Problem-solving approach** | Emphasis on interpreting data to guide decisions. | Emphasis on building models to automate decision-making. | |
||||
| **Domain knowledge** | Domain expertise in industries like healthcare, finance, marketing, etc. | Less reliance on specific domain knowledge; more generalizable algorithms. | |
||||
| **Software engineering** | Less focus on software engineering practices. | Strong focus on scalable system design and code optimization. | |
||||
| **Algorithm understanding** | Basic knowledge of algorithms for data analysis. | Deep understanding of algorithms, including neural networks and gradient descent. | |
||||
|
||||
Now that we've covered data science and machine learning regarding processes, tools, similarities, and differences, let's explore the key points you should consider to make the right career decision. |
||||
|
||||
## Data science vs. machine learning: Which career path fits your background? |
||||
|
||||
If you have a background in statistics, data analysis, and business intelligence, data science could be the perfect match for you. Data science is all about turning raw data into valuable insights that businesses can act on. Your familiarity with working with data makes it easier to spot patterns and trends, which is a key part of what data scientists do. It's a role that requires both creative problem-solving and analytical thinking. |
||||
|
||||
Machine learning, on the other hand, is better suited for you if you have a strong foundation in mathematics, programming, and computer science. A machine learning expert builds algorithms that can learn from data without explicitly programming them. It requires a solid grasp of concepts like linear algebra, calculus, probability, and algorithm design. If these are skills you already have, this path is a natural fit for you. |
||||
|
||||
## Data science vs. machine learning: Which path pays off in the long run? |
||||
|
||||
Both machine learning and data science offer exciting and rewarding career paths, especially with the growing demand for AI across industries. |
||||
|
||||
In data science, you typically start your career with entry-level positions like Data Analyst or Business Intelligence Analyst and can evolve into leadership roles like Chief Data Officer. This career path is appealing because it allows you to collaborate with both technical teams and business stakeholders, solving real-world problems with data-driven insights. |
||||
|
||||
A typical career progression in data science involves: |
||||
|
||||
- Data Analyst |
||||
- Data Scientist |
||||
- Senior Data Scientist |
||||
- Analytics Manager |
||||
- Chief Data Officer |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
Machine learning careers tend to offer slightly higher salaries due to the specialized skills in programming and algorithm design. A machine learning professional typically starts as a machine learning engineer and can progress to advanced roles like Head of AI/ML, focusing on developing intelligent systems and cutting-edge AI solutions. |
||||
|
||||
A typical career progression in machine learning involves: |
||||
|
||||
- Machine Learning Engineer |
||||
- AI Specialist |
||||
- Deep Learning Engineer |
||||
- AI Research Scientist |
||||
- Head of AI/ML |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
Both paths provide excellent growth opportunities, but your choice should align with your background and long-term career goals. |
||||
|
||||
## Data science vs. machine learning: Which opportunities are available for you? |
||||
|
||||
In terms of opportunities, data scientist are in higher demand across various industries that need data-driven insight to make decisions and improve their processes. These include companies within healthcare, finance, marketing, retail, and e-commerce. So, if your goal is to work in diverse industries that rely on data insights, then data science is an ideal choice. |
||||
|
||||
Machine learning, on the other hand, is more likely to work in technology-focused sectors where prediction, automation, and intelligence systems are at the core of their operation. These include industries like robotics, research and development labs, and autonomous vehicles. As a result, opportunities in machine learning may be harder to come by compared to data science, as machine learning professionals often work in more specialized and focused environments. However, if you're drawn to tech-driven fields involving autonomous systems or AI research, machine learning could be an ideal path for you. |
||||
|
||||
## Machine learning vs. data science: Which balances creativity and tech better? |
||||
|
||||
Data science strikes a balance between technical expertise and creativity. It's all about taking complex data and transforming it into meaningful insights that non-technical stakeholders can easily understand. If you enjoy solving problems creatively and telling compelling stories with data, data science would be a great fit for you. |
||||
|
||||
Machine learning, on the other hand, is more technical and involves developing algorithms. It involves designing, training, and optimizing models that enable machines to learn and make predictions. If you love tackling technical challenges like developing algorithms and building AI models from the ground up, then a career in machine learning would be ideal for you. |
||||
|
||||
As a rule of thumb, use the decision tree table to choose between data science and machine learning: |
||||
|
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
Choosing between data science and machine learning ultimately depends on your interests and career goals. Both fields offer rewarding opportunities and career growth. The key is to understand what excites you most: extracting meaning from data or building intelligent systems. |
||||
|
||||
If you're considering starting a career as a data scientist, explore our comprehensive [data science roadmap](https://roadmap.sh/ai-data-scientist) for actionable steps and valuable resources to get started. |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@ |
||||
--- |
||||
import GuideContent from '../../components/Guide/GuideContent.astro'; |
||||
import BaseLayout from '../../layouts/BaseLayout.astro'; |
||||
import { getGuideById } from '../../lib/guide'; |
||||
import { getOpenGraphImageUrl } from '../../lib/open-graph'; |
||||
import { replaceVariables } from '../../lib/markdown'; |
||||
|
||||
const guideId = 'ai-data-scientist-vs-machine-learning'; |
||||
const guide = await getGuideById(guideId); |
||||
|
||||
const { frontmatter: guideData } = guide!; |
||||
|
||||
const ogImageUrl = |
||||
guideData.seo.ogImageUrl || |
||||
getOpenGraphImageUrl({ |
||||
group: 'guide', |
||||
resourceId: guideId, |
||||
}); |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
<BaseLayout |
||||
title={guideData.seo.title} |
||||
description={guideData.seo.description} |
||||
permalink={`/ai-data-scientist/vs-machine-learning`} |
||||
canonicalUrl={guideData.canonicalUrl} |
||||
ogImageUrl={ogImageUrl} |
||||
> |
||||
<GuideContent guide={guide!} /> |
||||
<div slot='changelog-banner'></div> |
||||
</BaseLayout> |
||||
Loading…
Reference in new issue